Portal:History of science
The History of Science Portal
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Protoscience, early sciences, and natural philosophies such as alchemy and astrology during the Bronze Age, Iron Age, classical antiquity, and the Middle Ages declined during the early modern period after the establishment of formal disciplines of science in the Age of Enlightenment.
Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 to 1200 BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but continued to thrive in the Greek-speaking Byzantine Empire. Aided by translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Arabic-speaking Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The recovery and assimilation of Greek works and Islamic inquiries into Western Europe from the 10th to 13th century revived the learning of natural philosophy in the West. Traditions of early science were also developed in ancient India and separately in ancient China, the Chinese model having influenced Vietnam, Korea and Japan before Western exploration. Among the Pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica, the Zapotec civilization established their first known traditions of astronomy and mathematics for producing calendars, followed by other civilizations such as the Maya.
Natural philosophy was transformed during the Scientific Revolution in 16th- to 17th-century Europe, as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The New Science that emerged was more mechanistic in its worldview, more integrated with mathematics, and more reliable and open as its knowledge was based on a newly defined scientific method. More "revolutions" in subsequent centuries soon followed. The chemical revolution of the 18th century, for instance, introduced new quantitative methods and measurements for chemistry. In the 19th century, new perspectives regarding the conservation of energy, age of Earth, and evolution came into focus. And in the 20th century, new discoveries in genetics and physics laid the foundations for new sub disciplines such as molecular biology and particle physics. Moreover, industrial and military concerns as well as the increasing complexity of new research endeavors ushered in the era of "big science," particularly after World War II. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Africa has the world's oldest record of human technological achievement: the oldest surviving stone tools in the world have been found in eastern Africa, and later evidence for tool production by humans' hominin ancestors has been found across West, Central, Eastern and Southern Africa. The history of science and technology in Africa since then has, however, received relatively little attention compared to other regions of the world, despite notable African developments in mathematics, metallurgy, architecture, and other fields. (Full article...)
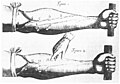
Selected image

An anthropometric device (side view) by Major A.J.N. Tremearne designed "for measuring the living head" for "the use of anthropologists", invented in 1913 with later additions made at the suggestion of A. Keith and Karl Pearson.
Did you know
... that the Merton Thesis—an argument connecting Protestant pietism with the rise of experimental science—dates back to Robert K. Merton's 1938 doctoral dissertation, which launched the historical sociology of science?
...that a number of scientific disciplines, such as computer science and seismology, emerged because of military funding?
...that the principle of conservation of energy was formulated independently by at least 12 individuals between 1830 and 1850?
Selected Biography -
Clarisse Doris Hellman Pepper (August 28, 1910 – March 28, 1973) was an American historian of science, "one of the first professional historians of science in the United States". She specialized in 16th- and 17th-century astronomy, wrote a book on the Great Comet of 1577, and was the translator of another book, a biography of Johannes Kepler. She became a professor at the Pratt Institute and later at the Queens College, City University of New York, and was recognized by membership in several selective academic societies. (Full article...)
Selected anniversaries
- 1852 - Birth of Henri Becquerel, French physicist, Nobel laureate (d. 1908)
- 1855 - Death of Jacques Charles François Sturm, French mathematician (b. 1803)
- 1913 - Birth of Roger Gaudry, French Canadian chemist, businessman and corporate director (d. 2001)
- 1916 - Birth of Maurice Wilkins, New Zealand-born physicist, Nobel laureate (d. 2004)
- 1923 - Birth of Freeman Dyson, English-born American physicist
- 1958 - Death of Wolfgang Ernst Pauli, Austrian-born American physicist, Nobel laureate (b. 1900)
Related portals
Topics
General images
Subcategories
Things you can do
Help out by participating in the History of Science Wikiproject (which also coordinates the histories of medicine, technology and philosophy of science) or join the discussion.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus